Shockwave Treatment
A New Wave of Relief for Muscle & Joint Pain
Looking for a non-surgical way to feel better and move more comfortably? Shockwave treatment is creating a new wave in musculoskeletal care by helping the body heal naturally. This innovative therapy uses gentle acoustic sound waves to stimulate blood flow, support tissue repair, and reduce pain, right at the source.
Many patients choose shockwave therapy because it’s quick, non-invasive, and requires little to no downtime. Whether you’re dealing with chronic muscle tension, tendon discomfort, or joint stiffness, shockwave treatment offers a modern, effective option to help you get back to doing what you love.
We’re proud to offer shockwave therapy as part of our commitment to advanced, patient-focused care, helping you move better, feel stronger, and live well.
Shockwave therapy has been used in medicine for decades. In the early 1980s, doctors in the United States began using high-energy sound waves to break up kidney stones without surgery. Over time, this same technology was refined and adapted to help treat muscle, tendon, and joint problems—without incisions or downtime.
Today, shockwave therapy is commonly used as a non-surgical treatment for many orthopedic and musculoskeletal conditions, and research is continuing to explore additional uses, including certain neurologic conditions like muscle tightness (spasticity).
What Is Shockwave Therapy?
Shockwave therapy uses acoustic (sound) waves that are applied through the skin to targeted areas of the body. These sound waves interact with tissues at a cellular level and help stimulate the body’s natural healing response.
There are two main types:
- Focused Shockwave Therapy (FSW):
Delivers energy deeper into specific tissues, often used for chronic or stubborn conditions. - Radial Pressure Wave Therapy (RPW):
Spreads energy over a broader area closer to the surface, often used for muscle pain and soft-tissue issues.
Both are non-invasive and performed in an outpatient setting.
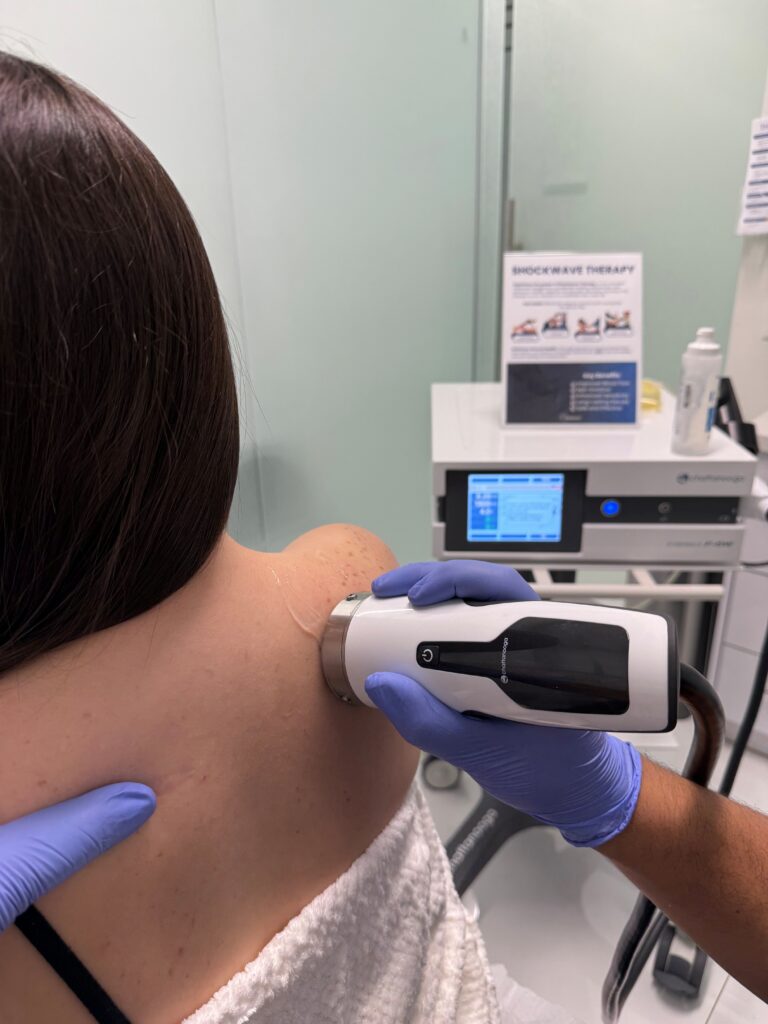
How Does It Help the Body Heal?
Shockwave therapy works through a process called mechanotransduction, which means mechanical energy (sound waves) is converted into biological signals inside your cells. This can lead to:

Increased blood flow and formation of new blood vessels

Reduced pain signaling

Stimulation of tissue repair and regeneration

Improved healing of tendons, ligaments, and bone

Support for healthy cell growth and movement
Common Benefits Patients May Experience
- Reduced pain and stiffness
- Improved mobility and function
- Faster healing without surgery
- Minimal recovery time
- Short treatment sessions
What Conditions Is It Commonly Used For?
Shockwave therapy is often used for:
- Tendon injuries (like plantar fasciitis or tennis elbow)
- Chronic muscle or joint pain
- Heel pain
- Shoulder, knee, or hip discomfort
- Certain neurologic conditions involving muscle tightness (emerging research)
Safety, Side Effects & Considerations
Shockwave therapy is generally well-tolerated. Some patients may experience:
- Mild soreness or redness at the treatment site
- Temporary swelling or tenderness
These effects usually resolve within a short time. Certain medical conditions may make shockwave therapy inappropriate, so a proper evaluation is always important before treatment.
FAQs
How does Shockwave Therapy work?
It uses high-energy acoustic waves to stimulate tissue repair, increase blood flow, and break down scar tissue reducing pain and improving mobility.
Who can benefit from Shockwave Therapy?
Anyone with chronic pain, tendonitis, overuse injuries, calcifications, or limited mobility can experience relief.
Is Shockwave Therapy safe?
Yes it’s non invasive, medication-free, and performed by trained professionals.
When will I see results?
Many patients feel improvement after 1–3 sessions, with continued progress over several weeks.
How many treatments do I need?
Most conditions improve with 4–8 sessions, depending on severity and treatment goals.
Schedule Your Appointment
If pain is limiting your quality of life, shockwave therapy may be the solution you’ve been looking for.

